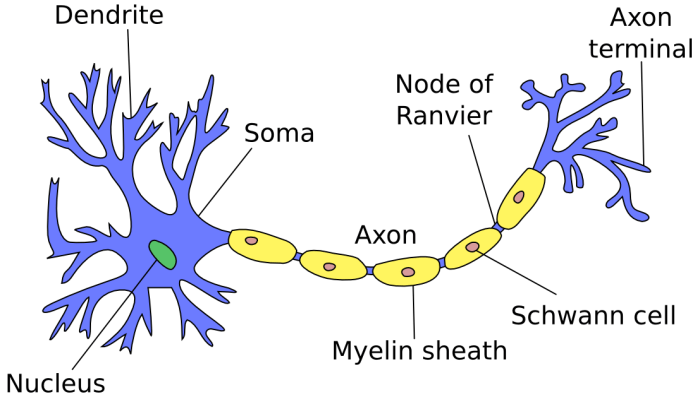
Unveiling the mystery behind the signal sending cells crossword clue, this discourse delves into the intricate realm of neuronal communication. Signal transmission, synaptic interactions, and the fascinating processes of signal integration and propagation unravel before us, painting a vivid picture of the brain’s intricate network.
Neurons, the fundamental units of signal transmission, generate electrical signals that relay information throughout the nervous system. Neurotransmitters, chemical messengers, facilitate signal exchange across synapses, the junctions between neurons. This intricate interplay orchestrates the brain’s ability to process and respond to stimuli.
Neuron Physiology: Signal Sending Cells Crossword Clue

Neurons are the fundamental units of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting electrical and chemical signals throughout the body. These signals allow neurons to communicate with each other and with other cells in the body.
Electrical Signals in Neurons
Electrical signals in neurons are generated by the movement of ions across the cell membrane. When a neuron is at rest, the inside of the cell is negative relative to the outside. This difference in electrical potential is called the resting membrane potential.
When a neuron receives a signal from another neuron, the membrane potential changes. This change in membrane potential is called an action potential. Action potentials are brief, all-or-nothing electrical pulses that travel along the axon of a neuron.
Role of Neurotransmitters in Signal Transmission, Signal sending cells crossword clue
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that are released by neurons to transmit signals to other neurons. When an action potential reaches the end of an axon, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron. These neurotransmitters then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, causing a change in the membrane potential of the postsynaptic neuron.
Types of Neurons Involved in Signal Sending
There are many different types of neurons involved in signal sending. Some of the most common types include:
- Sensory neurons: These neurons receive signals from the environment and transmit them to the central nervous system.
- Motor neurons: These neurons transmit signals from the central nervous system to muscles and glands.
- Interneurons: These neurons connect sensory neurons to motor neurons and are involved in processing and integrating information.
Synaptic Communication

Synapses are the junctions between neurons where signals are transmitted from one neuron to another. Synapses are composed of a presynaptic neuron, a postsynaptic neuron, and a synaptic cleft.
Structure and Function of Synapses
The presynaptic neuron is the neuron that sends the signal. The postsynaptic neuron is the neuron that receives the signal. The synaptic cleft is the space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons.
When an action potential reaches the presynaptic neuron, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron. These neurotransmitters then diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron.
Process of Synaptic Transmission
The process of synaptic transmission involves the following steps:
- Action potential arrives at the presynaptic neuron.
- Neurotransmitters are released from the presynaptic neuron.
- Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft.
- Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron.
- Postsynaptic neuron generates an action potential.
Factors that Modulate Synaptic Strength and Plasticity
The strength of a synapse is determined by the number of neurotransmitter receptors on the postsynaptic neuron and the affinity of the neurotransmitters for those receptors. The strength of a synapse can be modulated by a variety of factors, including:
- Activity-dependent plasticity: The strength of a synapse can be increased or decreased depending on the level of activity at the synapse.
- Neuromodulators: Neuromodulators are chemicals that can alter the strength of synapses.
- Drugs: Drugs can also alter the strength of synapses.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the primary function of signal sending cells?
Signal sending cells, also known as neurons, are responsible for transmitting information throughout the nervous system via electrical and chemical signals.
How do synapses contribute to signal transmission?
Synapses are specialized junctions between neurons that facilitate the transfer of signals across the neural network. Neurotransmitters released from the presynaptic neuron bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, triggering a response.
What factors influence the strength and plasticity of synapses?
The strength and plasticity of synapses are modulated by various factors, including the frequency and duration of neural activity, the availability of neurotransmitters, and the presence of neuromodulators.