Embark on an educational journey with the AP Statistics Chapter 7 Test, a comprehensive assessment that delves into the intricacies of hypothesis testing and data analysis. This guide will equip you with a thorough understanding of the test’s format, content, and strategies to ensure your success.
Prepare to delve into the fascinating world of statistical methods, where you will uncover the secrets of analyzing and interpreting data, drawing informed conclusions, and making data-driven decisions.
Test Overview
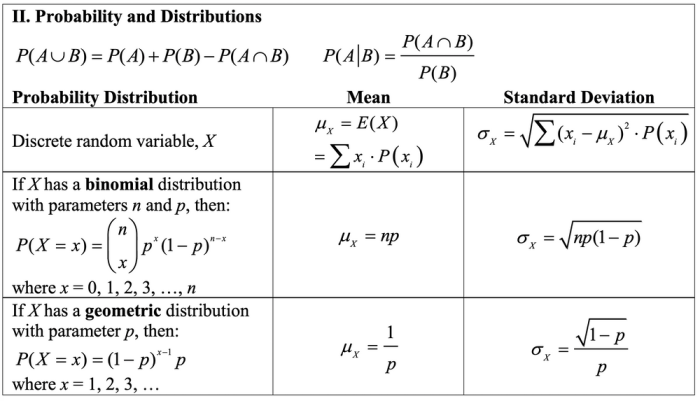
The Chapter 7 test assesses your understanding of the fundamental concepts of probability.
The test consists of multiple-choice questions, short-answer questions, and a few long-answer questions. It is designed to evaluate your ability to apply probability principles to real-world scenarios and solve problems involving probability distributions.
Test Format
- Multiple-choice questions: 20 questions, each worth 1 point
- Short-answer questions: 5 questions, each worth 2 points
- Long-answer questions: 3 questions, each worth 5 points
Duration and Grading, Ap statistics chapter 7 test
The test will last for 90 minutes. Your score will be based on the total number of points you earn, with the following grading scale:
- 90-100%: A
- 80-89%: B
- 70-79%: C
- 60-69%: D
- Below 60%: F
Content Coverage: Ap Statistics Chapter 7 Test
Chapter 7 delves into the intriguing world of hypothesis testing, providing a solid foundation for making informed decisions based on data. The test will evaluate your understanding of key concepts and your ability to apply them in various statistical scenarios.
AP Statistics Chapter 7 Test got you down? Check out q is the midpoint of pr for some helpful tips and tricks. Understanding this concept is crucial for tackling problems in the upcoming test. Keep practicing and don’t forget to utilize this valuable resource!
The specific learning objectives assessed in this test include:
Hypothesis Testing
- Understanding the concepts of null and alternative hypotheses
- Formulating hypotheses based on research questions
- Conducting hypothesis tests using appropriate statistical methods
- Interpreting p-values and making statistical decisions
Type I and Type II Errors
- Defining and understanding the concepts of Type I and Type II errors
- Calculating probabilities of Type I and Type II errors
- Minimizing the risk of making errors in hypothesis testing
Sample Size Determination
- Determining the appropriate sample size for hypothesis testing
- Understanding the factors that influence sample size
- Using statistical formulas to calculate sample size
Applications of Hypothesis Testing
- Applying hypothesis testing to real-world scenarios
- Interpreting results and making informed decisions
- Understanding the limitations and assumptions of hypothesis testing
Statistical Methods

Chapter 7 of AP Statistics introduces various statistical methods that are fundamental in analyzing data and drawing meaningful conclusions. These methods provide a systematic approach to understanding the underlying patterns and relationships within data sets, allowing researchers and analysts to make informed decisions.
Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method used to determine whether there is sufficient evidence to reject a null hypothesis, which typically represents the assumption that there is no significant difference or relationship between two or more variables. By comparing the observed data with the expected values under the null hypothesis, hypothesis testing allows researchers to make inferences about the population from which the sample was drawn.
Confidence Intervals
Confidence intervals are a range of values within which the true population parameter is likely to fall, with a specified level of confidence. They are constructed based on the sample data and provide an estimate of the population parameter with a certain degree of uncertainty.
Confidence intervals are widely used in various fields, such as opinion polls, medical research, and quality control.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a statistical method used to model the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. It allows researchers to predict the value of the dependent variable based on the values of the independent variables.
Regression analysis is commonly used in fields such as economics, finance, and social sciences to understand the factors that influence various outcomes.
Chi-Square Test
The chi-square test is a statistical method used to determine whether there is a significant difference between the observed frequencies of different categories in a data set and the expected frequencies under a certain assumption. It is commonly used in hypothesis testing to assess the independence of two categorical variables or to compare the proportions of different categories in a population.
Hypothesis Testing

Hypothesis testing is a fundamental statistical method that enables researchers to make inferences about a population based on a sample. It involves formulating a hypothesis, collecting data, and analyzing the data to determine whether the hypothesis is supported or rejected.
Hypothesis testing plays a crucial role in statistical analysis as it allows researchers to draw conclusions about the population they are studying. By testing hypotheses, researchers can determine whether their observations are due to chance or to a meaningful relationship between variables.
Steps Involved in Hypothesis Testing
- Formulate the Hypothesis:The researcher formulates a hypothesis, which is a statement about the population parameter being tested.
- Set the Significance Level:The researcher sets a significance level, which is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is actually true.
- Collect Data:Data is collected from a sample of the population being studied.
- Calculate the Test Statistic:A test statistic is calculated from the sample data to measure the difference between the observed data and the hypothesized value.
- Determine the P-value:The p-value is the probability of obtaining a test statistic as extreme as or more extreme than the one calculated from the sample data, assuming the null hypothesis is true.
- Make a Decision:The researcher compares the p-value to the significance level. If the p-value is less than the significance level, the null hypothesis is rejected; otherwise, it is not rejected.
Types of Hypothesis Tests
There are various types of hypothesis tests, each designed for specific research questions and data types:
- One-Sample Hypothesis Tests:Used to test hypotheses about a single population parameter, such as the mean or proportion.
- Two-Sample Hypothesis Tests:Used to compare two population parameters, such as the means or proportions of two different groups.
- Correlation Hypothesis Tests:Used to test the relationship between two variables, such as whether there is a correlation between height and weight.
- Chi-Square Hypothesis Tests:Used to test hypotheses about categorical data, such as whether the distribution of a categorical variable differs from a specified distribution.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Data analysis and interpretation are crucial aspects of statistical research. By employing statistical methods, we can uncover patterns, trends, and relationships within data, enabling us to draw meaningful conclusions and make informed decisions.
Visualizing and Summarizing Data
Visualizations, such as graphs and charts, are powerful tools for presenting data in a comprehensible and informative manner. These visuals allow us to quickly identify patterns, outliers, and trends that may not be apparent from raw data alone.
Additionally, statistical measures like mean, median, mode, and standard deviation provide numerical summaries of data, offering insights into its central tendencies and variability.
Common Pitfalls and Misconceptions
It is essential to be aware of common pitfalls and misconceptions when interpreting data. These include:
- Confirmation bias:The tendency to seek or interpret data that confirms existing beliefs or expectations.
- Overgeneralization:Drawing conclusions from a sample that is not representative of the population.
- Misinterpreting statistical significance:Failing to understand the difference between statistical significance and practical significance.
Test-Taking Strategies
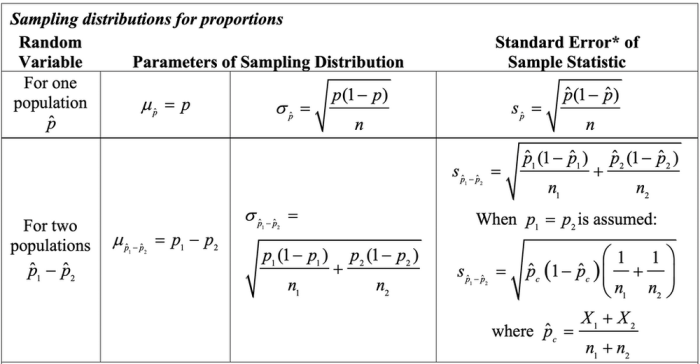
Preparing for and taking the Chapter 7 test requires effective strategies to maximize your performance. This section provides tips and techniques to help you excel in the exam.
Time Management
- Prioritize questions: Focus on completing the questions you know first to allocate more time to challenging ones.
- Estimate time per question: Dedicate a specific amount of time to each question to avoid spending too much time on any one.
- Don’t get stuck: If you’re struggling with a question, move on and return to it later to avoid wasting valuable time.
Effective Study Methods
- Review class notes and textbooks: Regularly review the material covered in class and your textbooks to reinforce your understanding.
- Practice problems: Solve practice problems from the textbook, online resources, or past exams to improve your problem-solving skills.
- Seek clarification: Don’t hesitate to ask your teacher or classmates for help with concepts you don’t understand.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Not reading instructions carefully: Read all instructions thoroughly before attempting to answer any questions.
- Guessing without justification: Provide clear reasoning and explanations for your answers, even if you’re unsure.
- Overconfidence: Don’t assume you know the material well enough without thorough preparation.
Quick FAQs
What is the purpose of the AP Statistics Chapter 7 Test?
The AP Statistics Chapter 7 Test evaluates your understanding of statistical methods, hypothesis testing, and data analysis, preparing you for college-level statistics courses.
What topics are covered on the test?
The test covers key concepts such as sampling distributions, confidence intervals, hypothesis testing, and data analysis techniques.
How can I prepare for the test?
Thoroughly review the course material, practice solving problems, and utilize study strategies Artikeld in this guide.